Microfluidic Devices - A Complete Analysis
Microfluidic devices contain individual chips that can process and manipulate very small amounts of liquids to perform certain desired tests. Hochuen Medical has pioneered its process and development to a great extent.
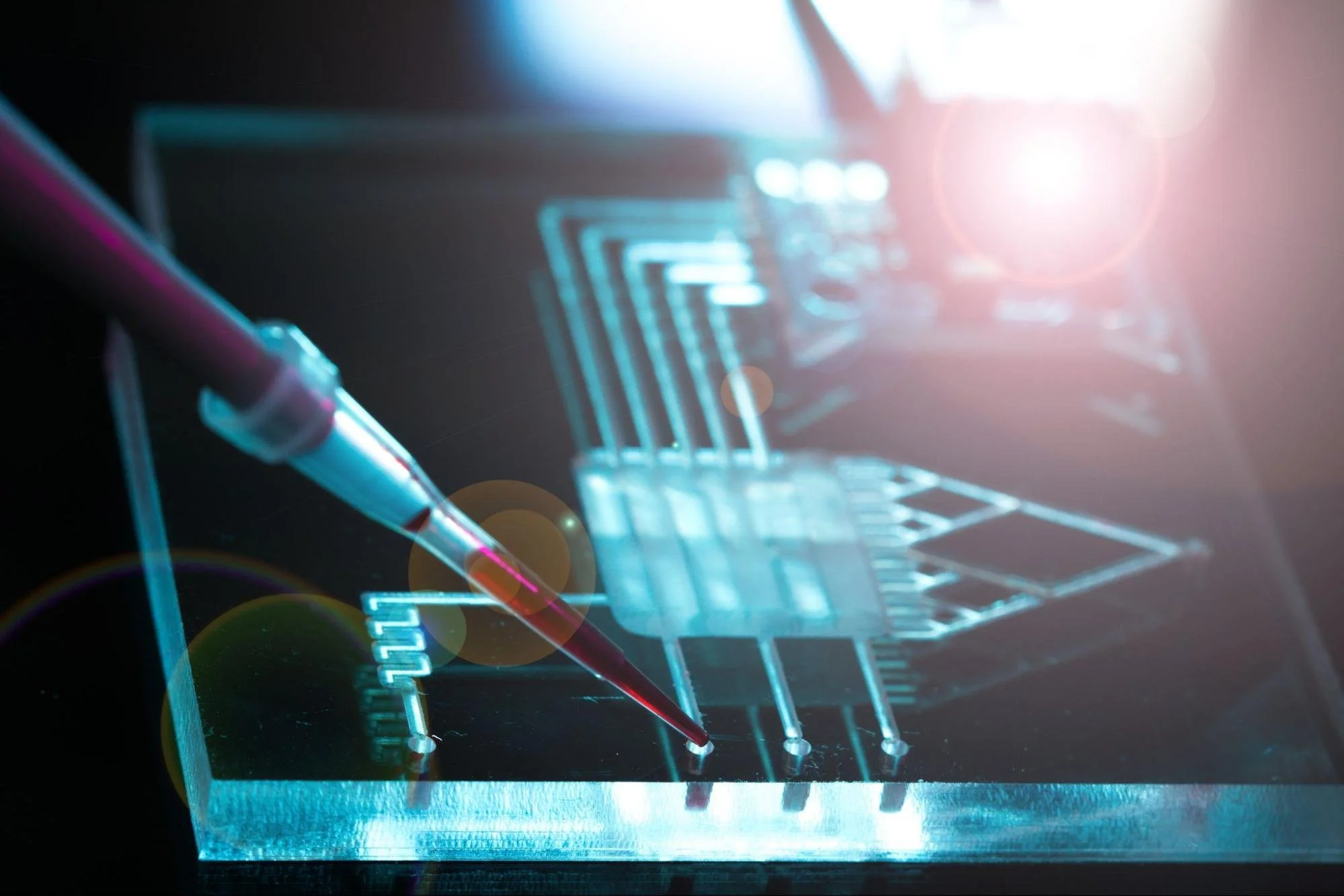
Microfluidic devices are built-in chips with a series of micro-channels imprinted into them. Some of these devices may be made of polymer, silicon, glass, or plastics like PDMS. To provide the best characteristics, the microfluidic chip's microchannels are joined together for controlling the biochemical environment.
How Do Microfluidic Devices Work?
A pump and a chip are used in microfluidic devices. Different types of pumps make the liquid circulation inside the chip at different rates, ranging from 1 liter to 10,000 liters per minute. Microfluidic channels are inducted into the chip, allowing for liquid processing such as chemical and physical reactions, as well as mixing. Small objects, such as nanoparticles(cells) can be carried by the liquid. The microfluidic devices enable the processing of these particles by way of the separation of cancer cells from healthy cells in the human bloodstream.
Why Use Microfluidic Devices?
Microfluidic devices can be used for a variety of purposes. Initially, a minute scale in the micron range will be applied. The ratio of the surface area to volume increases when the size of a 3D form decreases, such as a rectangular chamber or channel. The size increase makes microchannels ideal for capturing targets including cells, pathogens, and nanoparticles. Magnetic or electric fields are more effective over short distances, making microfluidic devices suitable for sensing and tracking. Another feature of microfluidics is the ability to observe and characterize small particles like living cells.
How to Make a Microfluidic Chip
Microfluidic chips are often made by cutting narrow grooves or small wells into a surface layer. Those features are then surrounded by a second layer to make microchannels. The layers must be correctly bonded to make the channels leak-proof. Hot embossing, soft lithography, micro-machining, injection molding, and etching are used to build the channels. Although 3D printing can be utilized to make microfluidic devices, it has significant restrictions in terms of reduced feature size, optical transparency, surface roughness, and material choice.
What are Droplet-Based Microfluidics?
In the field of microfluidics, droplet-based microfluidics has recently emerged as a leading technique. Droplet microfluidic devices produce very small droplets.
Droplet microfluidics have three key elements:
Molecular biology
Microparticle manufacturing
Microorganism investigations
Droplets are used as bioreactors in molecular biology. Single cells are captured in droplets. These cells then undergo a series of reactions that may be studied separately for each droplet. Hydrogel droplets are commonly used in microparticle synthesis, and they are further solidified after formation using chemical, thermal, and photo processing.
What is a DNA Chip?
A DNA chip is a device with thousands of pre-defined areas that are typically the size of a microscope slide. Each of these places has a different probe that can attach to a different target gene sequence.
What is a Biochip?
A biochip is a tiny device that connects an organism to a mechanical system directly. Biochips frequently have tiny built-in sensors that assess biochemical targets in substances like blood, skin, and cells. Microfluidics, microarrays, electronics, and optics are among the technological innovations used in biochips. Biochips are being used in illness diagnostics, security, and genetic analysis, with several other possibilities.
What are the Applications of Microfluidic Devices?
Microfluidic devices are used in almost every experimental science and engineering field. The most common uses are in the domain of molecular, cell biology, genetics, micro-mixing, chemical, protein synthesis, fluid dynamics, Lab on a Chip, Point of Care Diagnostics, Tissue culture, and many others.
Choosing the Best in Microfluidics
Since precise and regulated experiments can be carried out at a cheaper cost and a faster pace, microfluidic devices are becoming more popular in the sphere of biological sciences. Hochuen Medical has a long history of manufacturing and supplying the best microfluidic devices. Hochuen is one of the leading OEM manufacturers of microfluidic devices. We produce medical disposable devices for over 200 companies including Illumina, Roche, ThermoFisher, Siemens, Penumbra, Abcam, Heska, etc. We specialize in microfluidics and have capabilities in injection molding, die cutting, LSR, bonding (including laser welding, ultrasonic welding, heat staking, etc.), adhesives, lamination, laser micromachining, dry reagent handling, wet reagent blister packing, and many more.
Contact us to learn more about our contract manufacturing capabilities for microfluidic devices.